Basic knowledge
Mechanism of the spine
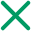
The spine, which is formally called the spinal column, comprises a series of 24 bones called the vertebrae. These vertebrae are classified into three types: 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae and 5 lumbar vertebrae. The spinal column, when seen from the front, appears to be straight, but seen sideways, has an S-shaped curve. When this sigmoid curvature cannot be maintained, the ligaments and intervertebral disks between the lumbar vertebrae and the muscles around the lumbar part cannot endure the excessive stress and undue pressure and stimulation are applied to the lumbar nerves.

Mechanism of the intervertebral disks
The intervertebral disks, which are located between vertebrae, serve as cushions that absorb impacts applied to the spinal column. They consist of a central pulpy nucleus and surrounding fibrous rings.
Backache is caused by a large variety of factors.
- Backache is a type of pain in which various factors are involved.
- Appropriate treatment and effective prevention depend on acquisition of correct knowledge on the causative factors.
Backache is a type of pain in which various factors are involved.
Appropriate treatment and effective prevention depend on acquisition of correct knowledge on the causative factors.
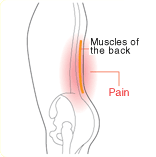
Osteoarthritis of the spine
Appropriate treatment and effective prevention depend on acquisition of correct knowledge on the causative factors.
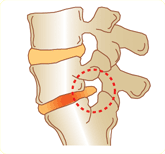
Lumbar disk herniation
The pulpy nucleus in the center of the intervertebral disk comes out of the gap, compresses the nerve root and causes lumbago, numbness and pain over the lower extremities.
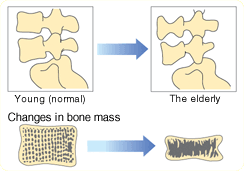
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is characterized by decreased bone density. Decreased lumbar bone density is regarded as the causative factor for extreme bone fragility, heavy feeling in the lumbar part and lumbago.
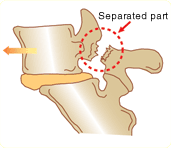
Lumbar spondylolysis (spondylolisthesis)
Part of a lumbar vertebra becomes separated. Excessive physical exercise during puberty may result in fatigue fractures of part of the lumbar vertebrae, leading to lumbar spondylolysis. If the separated condition is left untreated, the lumbar vertebra may move forward. This condition is called spondylolisthesis.
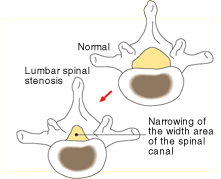
Lumbar spinal stenosis
Lumbar spinal stenosis occurs as a result of narrowing of the area of the spinal canal and subsequent compression of the nerves. Patients with lumbar spinal stenosis experience numbness and pain in the lower extremities during walking. Pain disappears when they stop walking and bend forward, but they experience recurrence of pain after starting walking again ("intermittent claudication").
Acute lower back pain
When we try to lift heavy things or take a kneeling position, we occasionally experience acute and paralyzing lower back pain. In this case, the muscles, vertebrae and intervertebral disks that support the spinal column have been injured.